
BG1899
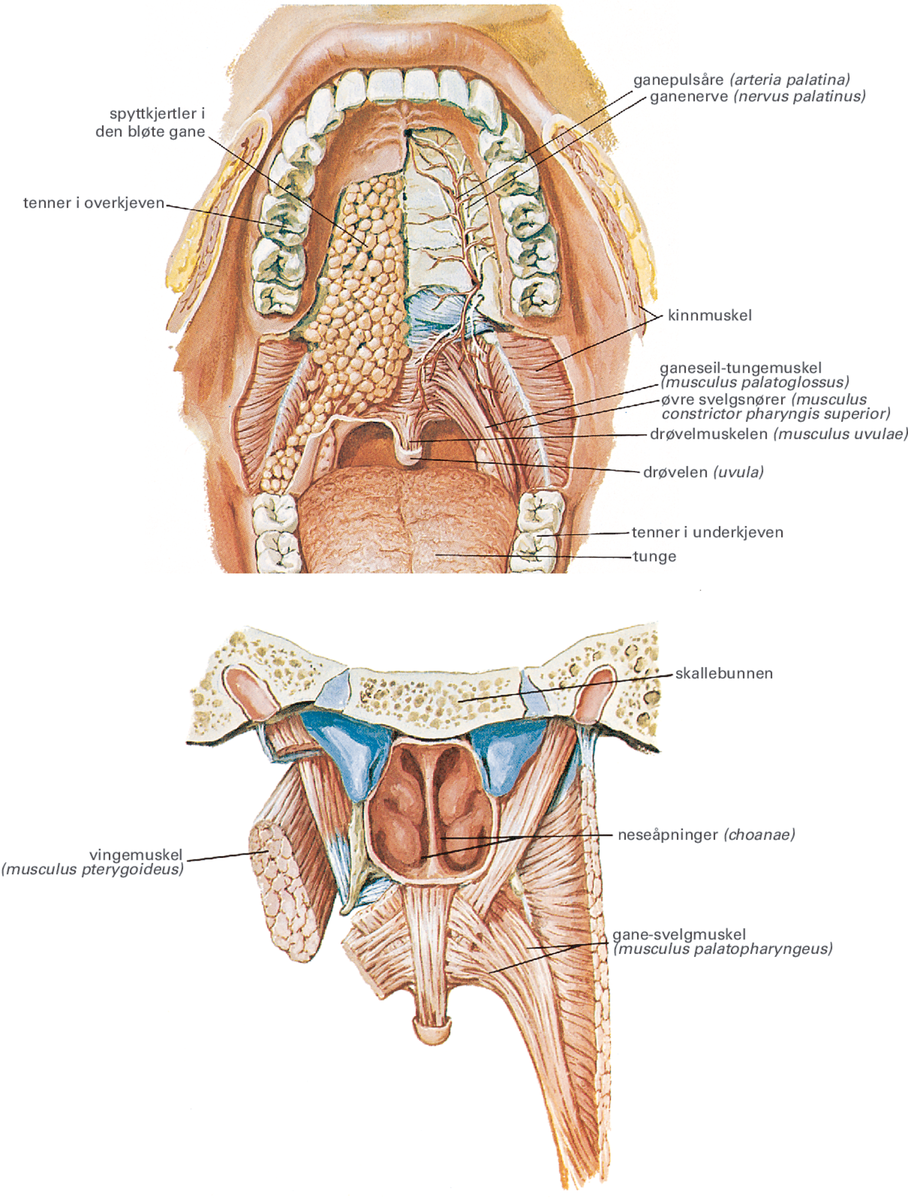
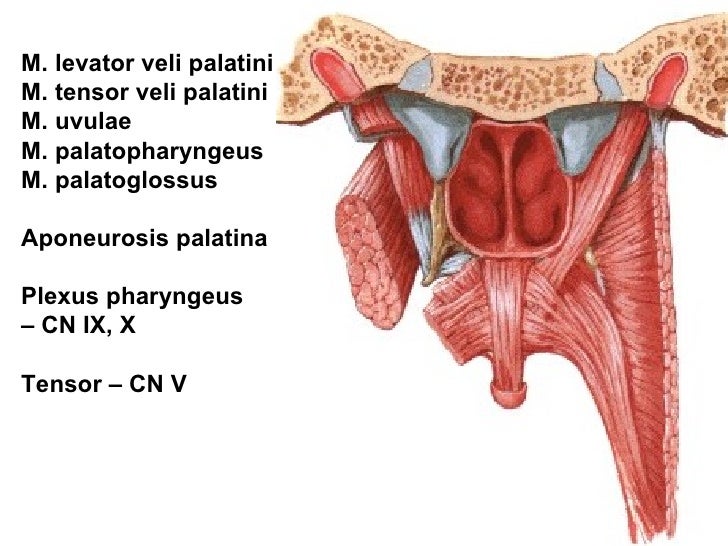
Palatopharyngeus is a longitudinal muscle that extends from the palate to the pharynx. Due to its length this muscle belongs to both the soft palate and pharyngeal muscle groups; Longitudinal muscles of the pharynx - together with salpingopharyngeus and stylopharyngeus.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7585/Palatoglossus_muscle_02.png)
Palatoglossus Muscle Function
The palatopharyngeal arch ( pharyngopalatine arch, posterior pillar of fauces) is larger and projects farther toward the middle line than the palatoglossal arch; it runs downward, lateralward, and backward to the side of the pharynx, and is formed by the projection of the palatopharyngeal muscle, covered by mucous membrane . References

PALATE INTRODUCTION Palate roof of the oral cavity
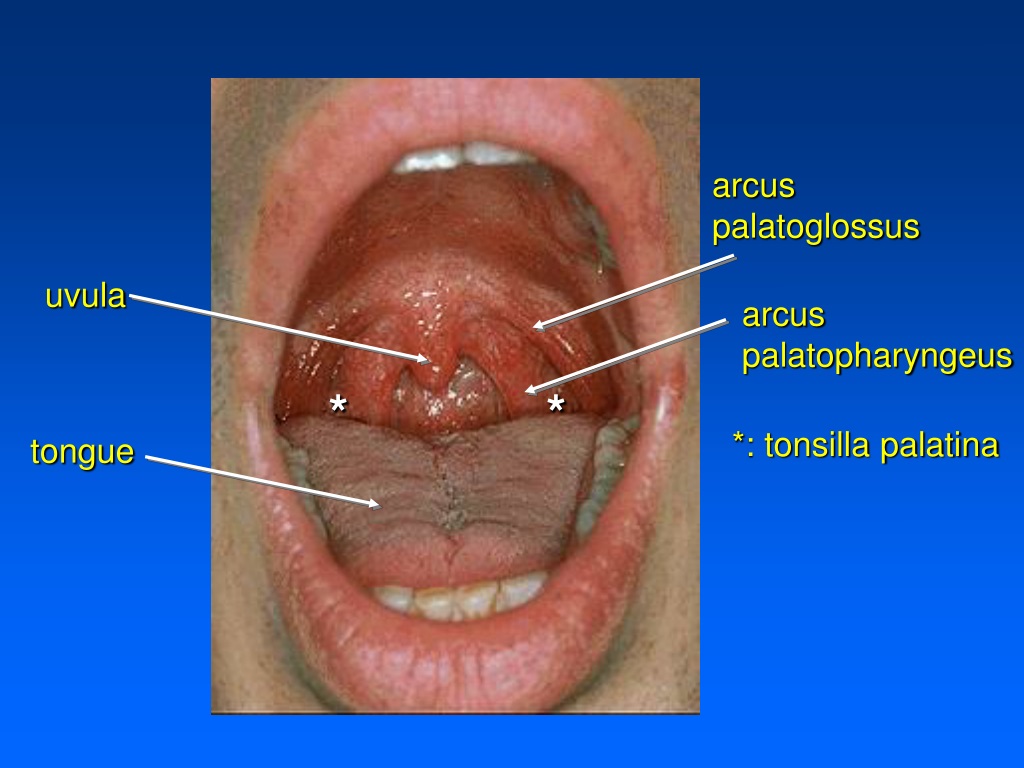
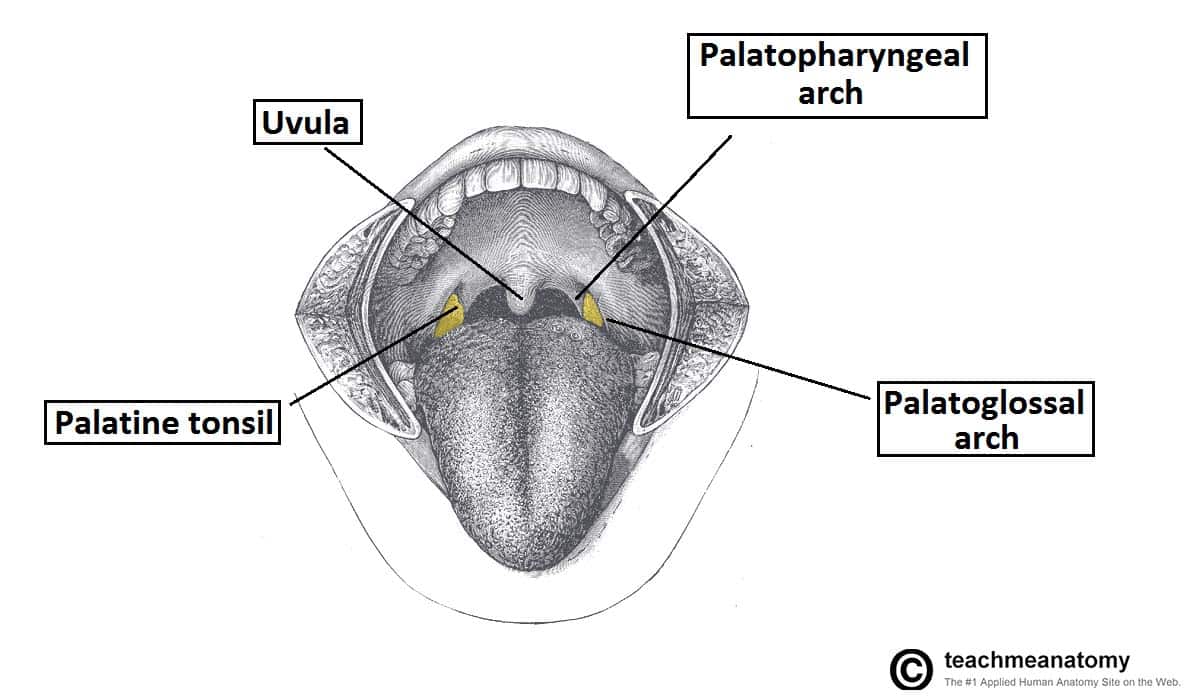
The palatopharyngeal arch (arcus palatopharyngeus), which is directed inferiorly to the lateral wall of the pharynx. Palatopharyngeal arch (arcus palatopharyngeus) Between both arches on each side, there is a tonsillar fossa or tonsillar sinus (fossa tonsillaris) , in which the palatine tonsil (tonsilla palatina) is located.

palatoglossus에 대한 이미지 검색결과 Orthodontics, Dental anatomy, Soft palate
Definition. Arching lateralward and downward from the base of the uvula on either side of the soft palate are two curved folds of mucous membrane, containing muscular fibers, called the palatoglossal arches (pillars of the fauces).

Oral Pharynx, with special reference to the Palatine Tonsil and the Musculature of the Palate
Arcus palatopharyngeus Read more Structure/ Morphology Key Features/ Anatomical Relations Slide Structure/Morphology There are two arches near the junction of the oral cavity and the oropharynx. These are the anterior palatoglossal and the posterior palatopharyngeal arches.
Oral Cavity & Pharynx (Week4) (Boundaries Cavity) (Oral Cavity Space…
The palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus, and stylopharyngeus muscles are intertwined with the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscles. Deep to the parapharyngeal space is the carotid sheath and its contents.
PPT Oral cavity, pharynx PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9730169
The pharyngopalatine arch (arcus pharyngopalatinus; posterior pillar of fauces) is larger and projects further toward the middle line than the anterior; it runs downward, lateralward, and backward to the side of the pharynx, and is formed by the projection of the Pharyngopalatinus, covered by mucous membrane. On either side the two arches are separated below by a triangular interval, in which.

PALATE INTRODUCTION Palate roof of the oral cavity
The morphology of the anatomic structures of the soft palate, the tonsillar fossae, and the palatoglossus and palatopharyngeal muscles is an important determinant of the size an. Life (Basel) . 2023 Mar 6;13(3):709. doi: 10.3390/life13030709.
The Pharynx Subdivisions Blood Supply TeachMeAnatomy
The palatopharyngeus ( palatopharyngeal or pharyngopalatinus) muscle is a small muscle in the roof of the mouth . It is a long, fleshy fasciculus, narrower in the middle than at either end, forming, with the mucous membrane covering its surface, the palatopharyngeal arch . Structure
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/2351/T3BW5k11f5MlfSpjOwpUw_the-muscles-of-the-tongue-sagittal_latin.jpg)
Musculus palatoglossus Anatomie & Funktion Kenhub
The oropharynx is the space in the back of the mouth, sometimes called the back of the throat. The base of the tongue, parts of the tonsil, the back of the soft palate, and the uvula are all located in the oropharynx. The oropharynx is often just called the pharynx. One of the first symptoms of pharyngeal cancer is a painless lump in the upper neck.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/5431/BTDMsBroiyRQRgx0XD9g_Palatoglossus_muscle_01.png.jpeg)
Passavant’s ridge Anatomy, muscles and clinical aspects Kenhub
The soft palate, also known as velum, is a mobile fold of soft tissue attached to the posterior margin of the hard palate. It extends posteroinferiorly, being leveled with the border between the nasopharynx and oropharynx. Unlike the hard palate, the soft palate doesn't contain a bony framework.

PALATE AND PALATINE MUSCLES ANATOMY wikitomy
The palatopharyngeus is a muscle of the pharynx.It is also considered to be a muscle of the soft palate. Attachments: Originates from the hard palate of the oral cavity and inserts onto the pharyngeal wall.; Actions: Elevates the pharynx during swallowing; Innervation: Vagus nerve (CN X).; Blood supply: Ascending pharyngeal artery (a branch of the external carotid artery) and tonsillar branch.
musculus palatopharyngeus Store medisinske leksikon
1) arcus palatoglossus - the anterior arch extends to the lateral margin of the tongue; 2) arcus palatopharyngeus - the posterior arch extends to the wall of the
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/palatoglossal-arch/ImLo3Lqx9qg3Hji5LiHgQ_Palatoglossal_arch_magnified.png)
Waldeyer’s Ring Definition, anatomy and pathology Kenhub
The palatoglossal arch ( glossopalatine arch, anterior pillar of fauces) on either side runs downward, lateral (to the side), and forward to the side of the base of the tongue, and is formed by the projection of the glossopalatine muscle with its covering mucous membrane.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12735/1bXEPFwhyKmS3BM2SKVqjQ_M._palatopharyngeus_01.png)
Palatopharyngeus Origin, insertion, innervation, action Kenhub
The palatopharyngeus muscle is a muscle of the head and neck, and one of the inner longitudinal muscles of the pharynx. It is also referred to as one of the five paired muscles of the soft palate . The paired muscles create ridges of mucous membrane in the lateral pharyngeal wall called the palatopharyngeal arches. Summary
1st week _digestive_system_i
The palatoglossus muscle is one of the four extrinsic muscles of the tongue. The paired muscles create ridges of mucous membrane in the lateral pharyngeal wall called the palatoglossal arches (also known as the anterior pillars of the fauces). These form the lateral boundary between the oral cavity anteriorly and the oropharynx posteriorly.